Accessibility – The design of products, devices, services, or environments for use by all people including those with (and without) disabilities. An accessible facility complies with applicable laws and regulations to ensure that services can be used with same degree of convenience, connection, and safety by everyone.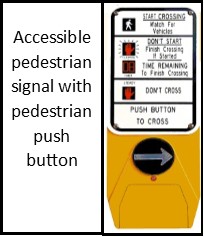
Accessible pedestrian signal with pedestrian push button – An integrated device that communicates information about the WALK and DON'T WALK intervals at signalized intersections in non-visual formats (i.e., audible tones and vibrotactile surfaces) to pedestrians who are blind or have low vision.
Curb ramp – A small ramp that cuts through or is built up to the edge (curb) of a sidewalk or path to ease passage to the street. 
Detectable warning device – A distinctive surface pattern of raised domes that are detectable by cane or underfoot. These alert people with vision impairments of their approach to a street crossing or hazardous drop-off.
Disability – A physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities, a record of such an impairment, or being regarded as having such an impairment. Individual with a disability means a person who has a disability.
Existing facility – A component of the infrastructure that is already in existence on any given date, without regard to whether the facility may also be considered newly constructed or altered.
Facility – In the context of this Plan, facility refers to any piece or component of transportation infrastructure in the public right-of-way.
Pedestrian access route – A continuous and unobstructed path of travel provided for pedestrians with disabilities within or coinciding with a pedestrian circulation path.
Public circulation path – A prepared exterior or interior surface provided for pedestrian travel.
Right-of-way – Public land or property, usually in interconnected corridors, that is acquired for or dedicated to public infrastructure. In this case, right-of-way is for transportation purposes. 
Slope – Also called incline or gradient. A difference in level or position between the two ends or sides of an object or facility (e.g., sidewalk or bike path). The slope is calculated by dividing the change in vertical height (“rise”) by the length (“run”). Slope is typically expressed as a percentage.
- Cross slope – The grade that is perpendicular to the direction of pedestrian travel. For example, the slope calculated across a sidewalk or bike path. To meet ADA guidelines, the cross slope needs to be 2% or less.
- Running slope – The grade that is parallel to the direction of pedestrian travel. For example, the slope calculated along a sidewalk or bike path. To meet ADA guidelines, the running slope needs to be 5% or less.

Surface discontinuity – A defect or difference in the outer layer of the pedestrian facility (e.g., sidewalk, bike path, pavement). Discontinuities can be vertical, where there is a height difference in the level between two adjoining surfaces or horizontal where there is a gap parallel to the ground.
